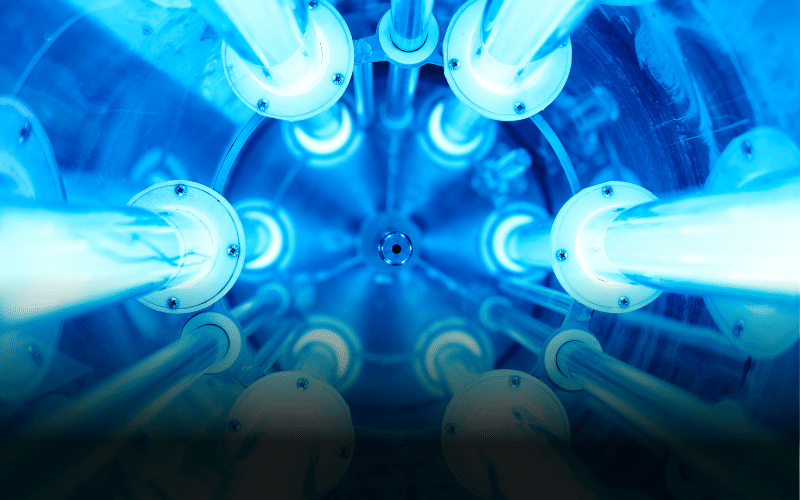
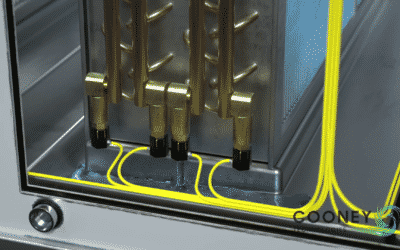
At the heart of our Cooney Thermo-Pack steam-to-water skid is a shell & coil heat exchanger. Let’s take a closer look at this high-efficiency heat exchanger, how the technology works, specs, and key benefits.
How do Shell & Coil Heat Exchangers work?
In a shell & coil heat exchanger, steam flows down the top connection through helically wound, corrugated stainless-steel tube bundles. The water for heating enters from the bottom connection and moves upward within the shell, absorbing latent heat transfer from the steam coils. This counterflow design optimizes efficiency by sub-cooling condensate. This leads to steam economy, elimination of flash steam, extended system life, and reduced maintenance costs.
Specifications:
- Engineered to sub-cool condensate, extracting maximum energy from each pound of steam
- 316L passivated electropolished stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance
- ASME Section VIII Division compliant with a maximum working pressure of 300 PSI and max temperature of 422°F
- Fully welded construction for structural integrity
Shell & Coil Heat Exchanger Benefits:
- Efficiency: The tightly packed steam tubes in the shell and coil create large heat transfer surface area in a compact design. By utilizing cross-counterflow sub-cooling, the Thermo-Pack maximizes energy efficiency by efficiently recovering heat from condensate.
- Maintenance: The complete stainless steel 316L welded construction ensures strength and durability. The corrosion-resistant materials reduce the need for frequent maintenance, promoting long-term reliability.
- Space Savings: The compact vertical footprint of the heat exchanger makes it ideal for installations in tight spaces. Additionally, the ability to manifold multiple units together allows for scalability without compromising space or efficiency.
How are Shell and Coil Heat Exchangers Different from Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
How Do Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Work?
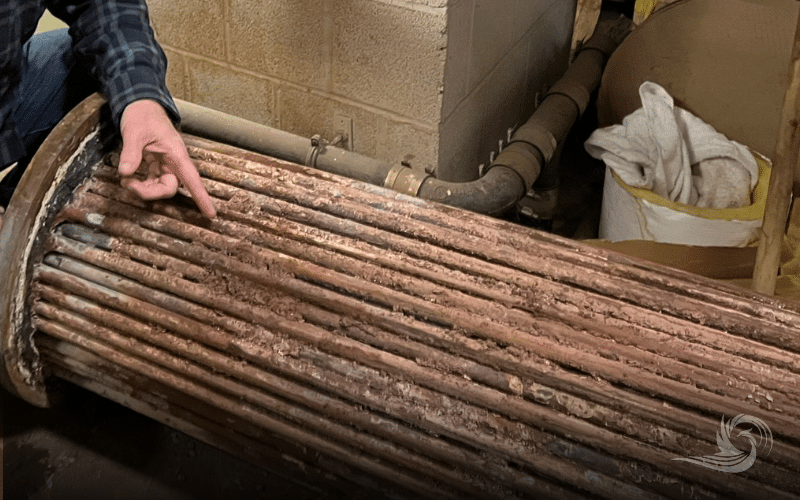
Shell-and-tube heat exchangers have often been used in industrial applications, hospitals, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The shell and tube heat exchanger made up of a shell vessel with tubes inside it. Steam fills the shell, while the liquid to be heated fills the tubes.
Key Differences:
- Footprint: Shell & coil heat exchangers have a smaller footprint compared to shell & tube exchangers due to their compact vertical design and tightly packed tube bundle. This makes them ideal for installations in tight spaces.
- Efficiency: The counterflow design of the shell and coil extracts more energy from the condensate creating steam savings and helping reduce carbon footprint. On average, facilities can expect a 10-15% in energy savings with a shell and coil compared to a traditional shell and tube heat exchanger.
- Maintenance: Shell and tube heat exchangers often have issues such as leaks, corrosion, and weakened tubes. This requires frequent attention and resources to address. Shell & coil heat exchangers have fully welded parts and are made of corrosion-resistant materials, making them more durable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cooney Thermo-Pack with shell & coil heat exchanger technology offers a blend of high efficiency, low maintenance, and space-saving design, making it a top choice for applications requiring reliable and energy-efficient steam-to-water heating solutions. Learn more about how Cooney Engineered Solutions can help you on your next project, contact us today!